Shortest Path Example
The shortest path algorithm implemented in graaf::algorithm::get_shortest_path can be used to compute the shortest
path between any two vertices in a graph.
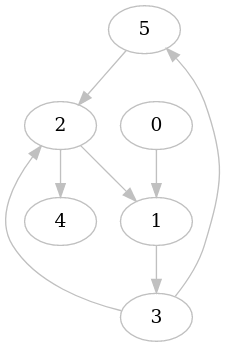
Consider the following graph:
In order to compute the shortest path between vertex 0 and vertex 2, we call:
const auto maybe_shortest_path{bfs_shortest_path(graph, start, target)};
// Assert that we found a path at all
assert(maybe_shortest_path.has_value());
auto shortest_path{maybe_shortest_path.value()};
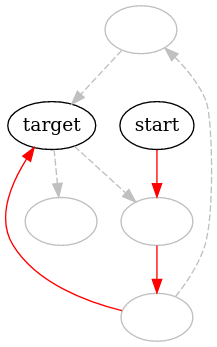
Visualizing the shortest path
If we want to visualize the shortest path on the graph, we can create our own vertex and edge writers. These writers then determine the vertex and edge attributes based on whether the vertex or edge is contained in the shortest path.
First, we create a datastructure of all edges on the shortest path such that we can query it in the edge writer:
// We use a set here for O(1) time contains checks
std::unordered_set<graaf::edge_id_t, graaf::vertex_ids_hash> edges_on_shortest_path{};
// Convert the list of vertices on the shortest path to edges
graaf::vertex_id_t prev{shortest_path.vertices.front()};
shortest_path.vertices.pop_front();
for (const auto current : shortest_path.vertices) {
edges_on_shortest_path.insert(std::make_pair(prev, current));
prev = current;
}
Now we can specify our custom writers:
const auto vertex_writer{
[start, target](graaf::vertex_id_t vertex_id, int vertex) -> std::string {
if (vertex_id == start) {
return "label=start";
} else if (vertex_id == target) {
return "label=target";
}
return "label=\"\"";
}};
const auto edge_writer{
[&edges_on_shortest_path](const graaf::edge_id_t& edge_id, int edge) -> std::string {
if (edges_on_shortest_path.contains(edge_id)) {
return "label=\"\", color=red";
}
return "label=\"\", color=gray, style=dashed";
}};
This yields us the following visualization: